GitHub 链接:HTTPS://GitHub.com/UriPomer/Unity-Path-Tracing
本人去年(2024)中旬开始想入门一点图形学,有点感兴趣,也对我的职业生涯有帮助,于是当时两周入门,并写了这个项目。后来因为其他事情一直搁置,最近心血来潮把他的效果修正了,帧数还不太高。
等下一次心血来潮的时候,继续学习,优化到实时渲染的水平
现在长这样:
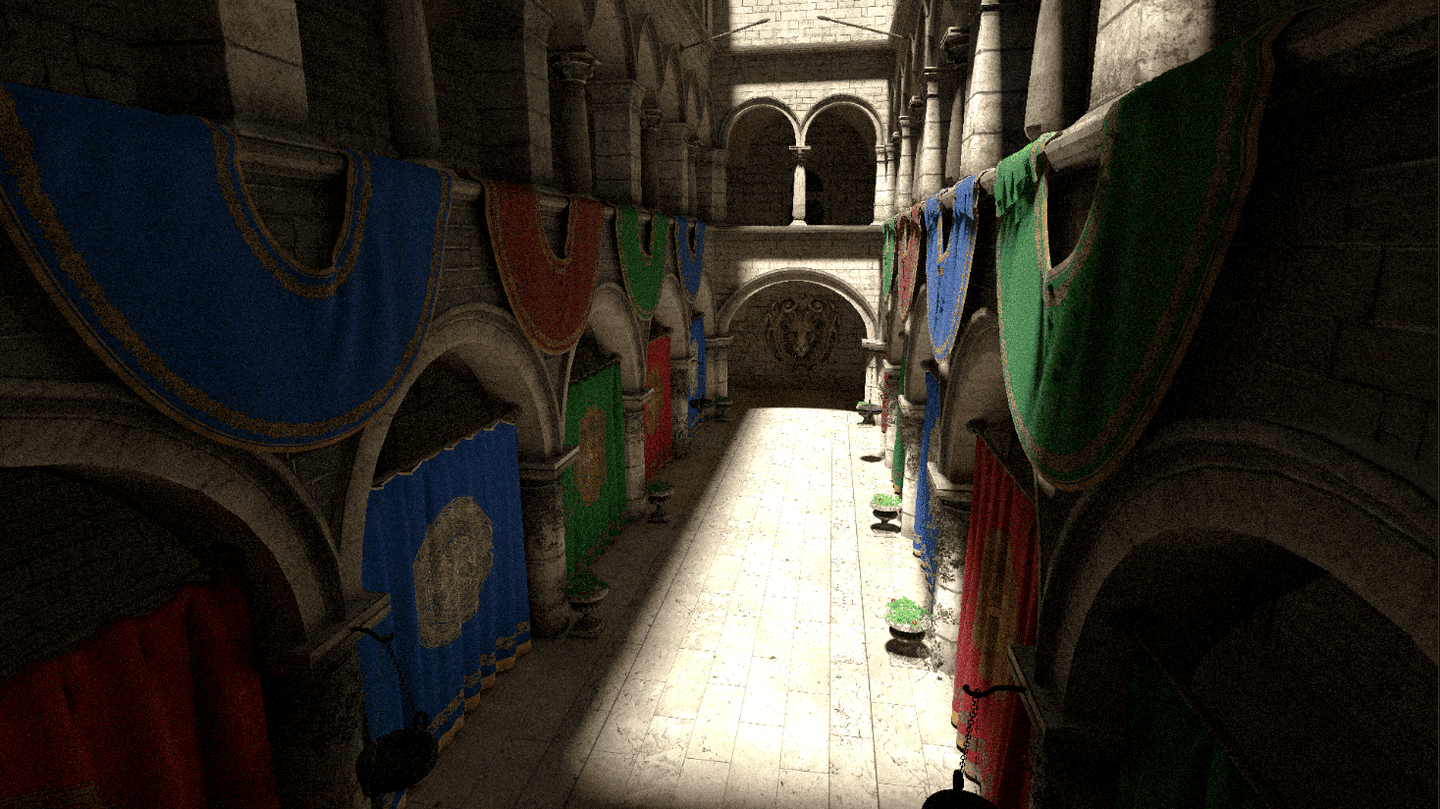
中间长这样:
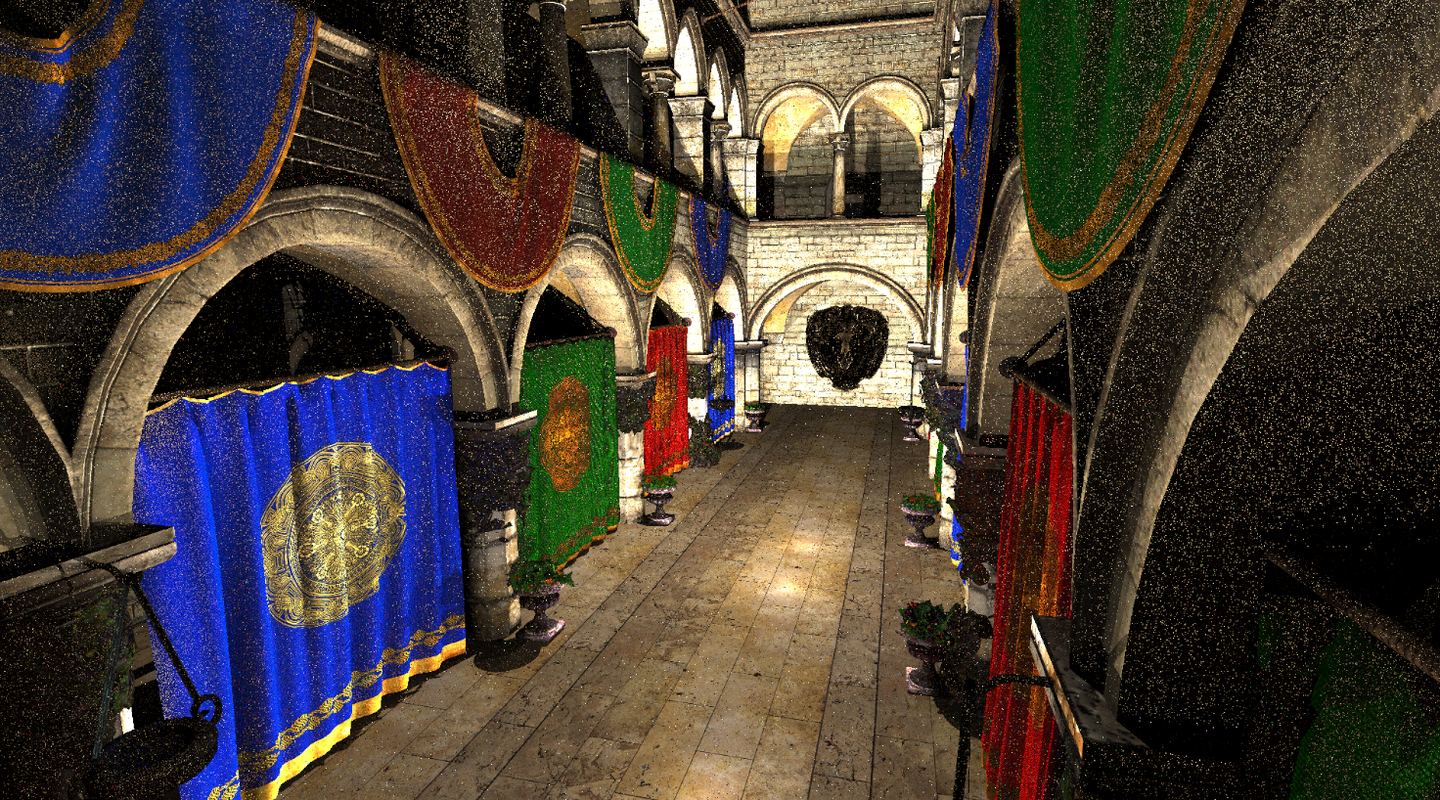
一开始长这样的:

一、项目概览
概览:在 Unity 中用 ComputeShader 实现一套真实感强、性能可控的实时光线追踪管线。 多阶段优化:从纯球体→BVH→多材质→PBR 无偏估计(Russian Roulette) Cook–Torrance 微表面 BRDF 软阴影、多光源支持
性能:通过内存带宽与算法优化,复杂场景 FPS 从 ~1.7 提升至 ~37;简单场景可达 120 FPS 以上。
二、渲染方程(Rendering Equation)
在路径追踪(Path Tracing)中,我们解决经典的 Kajiya 渲染方程:
Lo(x,ωo)=Le(x,ωo)+∫Ωfr(x,ωi,ωo)Li(x,ωi)(n⋅ωi)dωi
算法思路:
采样:每次击中,随机采样一个方向 ωi
无偏估计:利用 Russian Roulette 控制路径长度
累加:将 frLi(n⋅ωi)/pdf 累加到辐射贡献
由于我有点光源和自发光物体,我会在每次 bounce 都显示对光进行采样,代码中 Li、余弦项、pdf、fr 都是分开解耦的。
三、光照模型 —— Cook–Torrance 微表面 BRDF
我们采用经典的 Cook–Torrance 模型,将 BRDF 拆分为以下三部分:
分布函数 D(h):GGX 法线分布
几何遮蔽函数 G(v,l):Smith GGX
菲涅尔项 F(v,h):Schlick 近似或精确 Dielectric
最终:
fr(n,v,l)=D(h)G(v,l)F(v,h)4(n⋅v)(n⋅l)
α:粗糙度平方
核心 HLSL 实现
hlsl
复制编辑
// 菲涅尔——Schlick 近似
float3 SchlickFresnel(float cosTheta, float3 F0)
{
return lerp(F0, 1.0, pow(1.0 - cosTheta, 5.0));
}
// GGX 法线分布
float DistributionGGX(float3 N, float3 H, float alpha)
{
float NdotH = saturate(dot(N,H));
float a2 = alpha*alpha, d = NdotH*NdotH*(a2-1.0)+1.0;
return a2 / (PI * d * d);
}
// Smith GGX 遮蔽—蒙版函数
float SmithG(float NdotV, float alpha)
{
float a2 = alpha*alpha, b = NdotV*NdotV;
return (2.0*NdotV)/(NdotV + sqrt(a2 + b - a2*b));
}
float GeometrySmith(float3 N, float3 V, float3 L, float alpha)
{
return SmithG(saturate(dot(N,V)),alpha)
* SmithG(saturate(dot(N,L)),alpha);
}
// 组合 Specular BRDF
void SpecReflModel(RayHit hit, float3 V, float3 L, float3 H,
out float3 f_brdf, out float pdf)
{
float NdotV = saturate(dot(hit.normal,V));
float NdotL = saturate(dot(hit.normal,L));
float3 F0 = lerp(float3(0.04), hit.material.albedo, hit.material.metallic);
float alpha = hit.material.roughness * hit.material.roughness;
float3 F = SchlickFresnel(dot(V,H), F0);
float D = DistributionGGX(hit.normal,H,alpha);
float G = GeometrySmith(hit.normal,V,L,alpha);
f_brdf = F * G * D / max(4.0 * NdotV * NdotL, 1e-4);
pdf = (D * dot(hit.normal,H)) / max(4.0 * dot(V,H), 1e-4);
}
Tip:为了改善重要性采样效果,我们使用 GGX VNDF(可参考 SampleGGXVNDF 函数)来准确采样微表面法线分布。
四、路径追踪主循环
在 Shade(Ray ray) 中,进行最多 _TraceDepth 次弹跳:
hlsl
复制编辑
float3 Shade(Ray ray)
{
float3 throughput = 1, L_total = 0;
for (int b = 0; b < _TraceDepth; ++b)
{
RayHit hit = Trace(ray);
if (hit.distance == INF) { L_total += throughput * SampleSkybox(ray); break; }
// 自发光
if (hit.material.emissionIntensity > 0)
L_total += throughput * hit.material.emission * hit.material.emissionIntensity;
float3 V = -ray.dir;
// 计算反射/折射方向并更新 throughput
// …(见上文 SpecReflModel / SpecRefrModel)
// 直接光:多光源迭代
float3 Lo = GetLightContribution(hit, ray.dir);
L_total += throughput * Lo;
// Russian Roulette
float p = max(max(throughput.r, throughput.g), throughput.b);
if (RNG_Next(rng) >= p) break;
throughput /= p;
// 更新射线
ray.origin = hit.position + hit.normal * 1e-5;
ray.invDir = 1.0 / ray.dir;
}
return L_total;
}
Trace:BVH 加速的光线求交
Russian Roulette:当 throughput 很小时,随机终止以降低计算量
多光源:GetLightContribution 累加直射光贡献


